In the world of high-performance computing and artificial intelligence, selecting the right GPU can be a game-changer. For many organizations and individuals, the cost of top-tier GPUs like the NVIDIA A100 or H100 can be a barrier. Fortunately, more cost-effective options like the NVIDIA A40 and RTX A6000 offer substantial performance without breaking the bank.
Overview: A40 vs. RTX A6000
The NVIDIA A40 and RTX A6000 are two powerful GPUs designed to cater to different environments. The A40 is optimized for server settings, while the RTX A6000 is tailored for desktop workstations. Both GPUs leverage the Ampere architecture, delivering robust performance and advanced features for various demanding applications.
NVIDIA A40
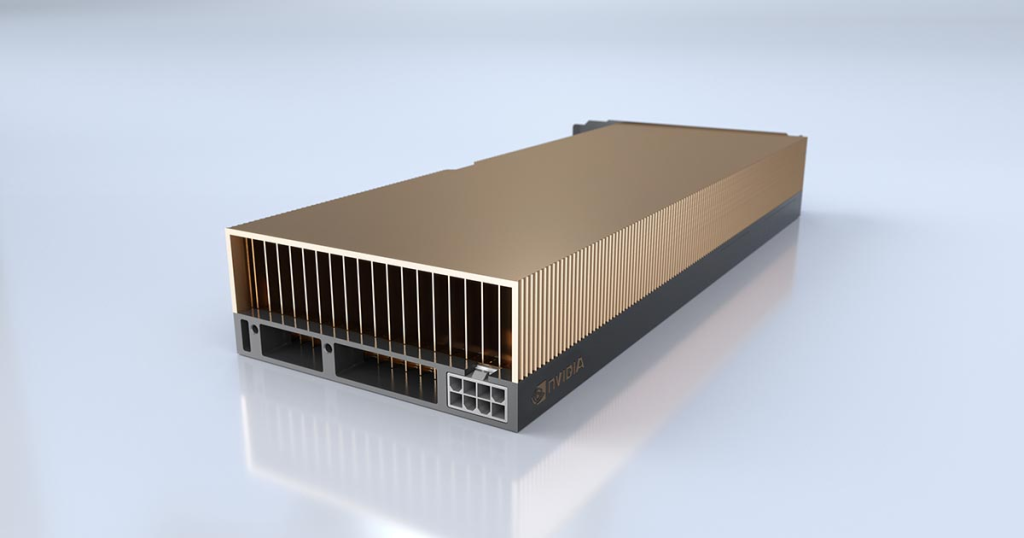

The NVIDIA A40 is a robust GPU tailored for data centers and high-performance computing. It delivers reliable performance for AI and deep learning with ample memory and advanced cores. Its passive cooling system is designed for efficient operation in server environments, making it an ideal choice for virtualized and cloud-based applications.
NVIDIA RTX A6000
The NVIDIA RTX A6000 is a premier GPU for professional workstations and content creation. It features significant memory and an active cooling system to handle demanding applications. With its advanced cores, the RTX A6000 excels in AI, deep learning, and high-end visualization, offering exceptional performance for rendering and computational tasks.
Key Features of A40 and RTX A6000
While both the A40 and RTX A6000 share a foundation in NVIDIA’s Ampere architecture and offer 48GB of GDDR6 memory with error correction, they have distinct characteristics suited to their intended uses.
- Architecture and Memory: Both GPUs are built on the Ampere architecture and feature 48GB of GDDR6 memory. They support ECC (Error-Correcting Code), ensuring data integrity during complex computations.
- Performance Metrics: The A6000 slightly outpaces the A40 with its higher memory bandwidth and clock speed. This translates to a performance edge, especially in memory-intensive tasks.
- Cooling and Power: The A40 employs a passive cooling system ideal for server environments, whereas the RTX A6000 uses an active cooling system suited for workstations. Both GPUs have a maximum power consumption of 300 watts.
Comparing Specifications
Here’s a comparative look at the specifications for both GPUs:
| Feature | NVIDIA A40 | NVIDIA RTX A6000 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Ampere | Ampere |
| Memory Size | 48 GB | 48 GB |
| Memory Type | GDDR6 | GDDR6 |
| Error-Correcting Code (ECC) | Yes | Yes |
| CUDA Cores | 10,752 | 10,752 |
| Tensor Cores | 336 | 336 |
| Ray-Tracing Cores | 84 | 84 |
| Memory Bandwidth | 696 GB/s | 768 GB/s |
| Clock Speed | 1305 MHz | 1410 MHz |
| Boost Speed | 1740 MHz | 1800 MHz |
| Memory Clock | 1812 MHz (14.5 Gbps effective) | 2000 MHz (16 Gbps effective) |
| Cooling Solution | Passive | Active |
| Power Consumption | 300 W | 300 W |
| Display Ports | 3x DisplayPort 1.4 | 4x DisplayPort 1.4 |
| NVLink Support | Yes | Yes |
Applications and Benefits
The NVIDIA A40 and RTX A6000 are versatile GPUs that cater to various applications:
- AI and Deep Learning: Ideal for training and fine-tuning neural networks, running AI inference, and deploying applications across sectors like healthcare and finance.
- Scientific Research: Useful for simulations, modeling, and data analysis in fields such as bioinformatics and climate studies.
- Advanced Visualization: Perfect for tasks requiring high rendering speeds and visual fidelity, including content creation, graphic design, and animation.
Conclusion
Choosing between the NVIDIA A40 and RTX A6000 largely depends on your specific needs and environment. The RTX A6000 offers slightly better performance with higher memory bandwidth and clock speeds, making it suitable for high-end desktop workstations. In contrast, the A40’s passive cooling and network-ready features make it an excellent choice for server environments.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.